In Healthcare today, there is a tremendous need for well-validated biomarkers to objectively monitor red blood cell health. At Functional Fluidics our red blood cell function biomarkers support these evolving needs.
Functional Fluidics is a high complexity CLIA-certified diagnostic lab. Our mission is to be the gold standard in red blood cell health starting with Sickle Cell Disease.
Our suite of assays is currently offered nationally to clinical providers, pharmaceutical, academic and biotech partners to support drug development and patient care.
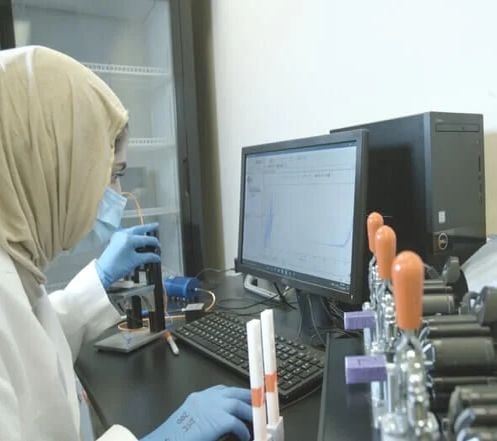

Functional Fluidics provides contract research services to pharmaceutical, BioTech and academic research companies. We are well-positioned to address the needs of clients with large-scale validation studies and to provide insights into the individual patient-level response critical for development of personalized medical applications.
Our suite of proprietary cell function assays can help validate assumptions or support clinical claims. If your organization is in the Pre-Clinical, Clinical or Post-Marketing research stage, you can benefit from our biomarkers and our expertise in defining Red Blood Cell Health.

Value-added services for our pharma partners to help accelerate clinical trials
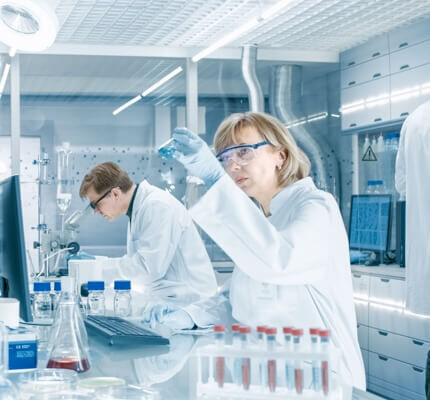

Biomarker specialty lab with proprietary biomarker assays to support the advancement of red blood cell therapies.

As we continue our growth, we invite those interested in investing our expansion to engage with our team.
This short video describes the origins of the company, based on research in the Hines Lab at Wayne State University. We have developed a suite of assays that address the need for better ways to assess blood function, starting with the experience of Dr. Hines as a Pediatric ICU Physician at Detroit Medical Center.

Proprietary Lab Tests
.png?width=80&name=New%20Project(1).png)
CLIA Certified Lab
.png?width=106&name=New%20Project(5).png)
Complex Tests Experience
.png?width=106&name=New%20Project(2).png)
Thought Leader Access
.png?width=80&name=New%20Project(3).png)
Specialized Staff
.png?width=106&name=New%20Project(4).png)
Strong Industry Relationships
Our suite of proprietary cell function assays can help validate assumptions or support clinical claims.
Evaluation of Longitudinal Pain Study in Sickle Cell Disease (ELIPSIS) by Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes, Actigraphy, and Biomarkers
This non interventional, longitudinal, 6-month study aimed to develop tools to identify VOCs in SCD patients with or without health care utilization.
Red Blood Cell Mechanical Fragility as Potential Metric for Assessing Blood Damage Caused by Implantable Durable Ventricular Assist Devices: Comparison of Two Types of Centrifugal Flow Left Ventricular Assist Devices.
Implantable Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs) have become a treatment of choice for patients with end-stage heart failure or cardiogenic shock, significantly increasing both survival rates and the quality of life of patients.
Individual Variability in Response to a Single Sickling Event for Normal, Sickle Cell, and Sickle Trait Erythrocytes
Hemoglobin S (Hb-S) polymerization is the primary event in sickle cell disease causing irreversible damage to red blood cell (RBC) membranes over repeated polymerization cycles.
Sevuparin blocks sickle blood cell adhesion and sickleleucocyte rolling on immobilized L-selectin in a dose dependent manner
Adhesion of sickle red blood cells (SSRBC) to the vascular endothelium may initiate and propagate vascular obstruction in sickle cell disease (SCD)
Impact of Environment on Red Blood Cell ability to Withstand Mechanical Stress.
Susceptibility of red blood cells (RBC) to hemolysis under mechanical stress is represented by RBC mechanical fragility (MF), with different types or intensities of stress potentially emphasizing different perturbations of RBC membranes
An Approach to Measuring RBC Haemolysis and Profiling RBC Mechanical Fragility
Red blood cells (RBC) can be damaged by medical products, from storage or from disease. Haemolysis (cell rupture and haemoglobin release) is often a key indicator, with mechanical fragility (MF) offering the potential to assess sub-haemolytic damage as well
Low Molecular Weight Heparin Inhibits Sickle Erythrocyte Adhesion to VCAM-1 through VLA-4 Blockade in a Standardized Microfluidic Flow Adhesion Assay
The vaso-occlusive events in sickle cell disease (SCD) begin in early childhood, warranting the need for more preventative and therapeutic interventions for those affected
Impact of the Oscillating Bead Size and Shape on Induced Mechanical Stress on Red Blood Cells and Associated Hemolysis in Bead Milling
While in circulation, red blood cells (RBC) need to elastically undergo large deformations without lysing, an ability that may be compromised by cell membrane damage.
440 Burroughs Street,
Suite 447, Detroit, MI 48202
United States
© Copyright Functional Fluidics 2016.